Introduction
In today’s world, where the amount of regulations and laws is constantly increasing, the effective management of compliance risks is a central element of corporate governance. Non-compliance with regulatory requirements can result in significant legal and financial consequences. This is evident in the numerous headlines about companies that have committed compliance violations. Indeed, compliance risks affect every company, whether it is a public, private, for-profit, non-profit, government or federal organization.
Thus, a thorough compliance risk analysis is essential to be best prepared for such incidents. While it does not allow for accurate predictions for the future, it does provide insight into which areas of the business, which processes, and which areas of law are more likely to have compliance violations and where there are fewer risks.
Since a compliance risk analysis is critical to building a robust compliance management system, this blog post will take a closer look at it.
What is compliance risks?
Compliance risks are potential dangers resulting from individual or collective misconduct by employees, executives or the management of a company. These risks manifest themselves in a variety of ways and can affect a company’s reputation, legal liability, and economic stability. Compliance violations can result in significant financial damage, including fines, loss of reputation, and claims for damages.
To successfully counter compliance violations, a comprehensive risk analysis is therefore crucial. It forms the basis of a sustainable and effective compliance program. Without a compliance risk analysis, companies run the risk of setting the wrong priorities, taking ineffective measures and overlooking relevant risks. Compliance risk analysis should ideally be performed at the beginning of a company’s compliance efforts. It involves three basic steps: identifying risks, assessing their impact, and deriving measures to minimize those risks. Let’s take a closer look at each of these steps in the following sections.
Compliance risk mitigation in 3 simple steps
Step 1- Compliance risk identification
Compliance risks extend across various areas of law, regulations, and ethical and moral principles, such as those set out in a company’s code of conduct. However, the exact nature of these risks varies from company to company. Particular attention should be paid to areas of law that are frequently associated with high risks of damage. These include, for example, data protection, IT security, corruption and fraud, export control, labor law, environmental protection, and antitrust and competition law.
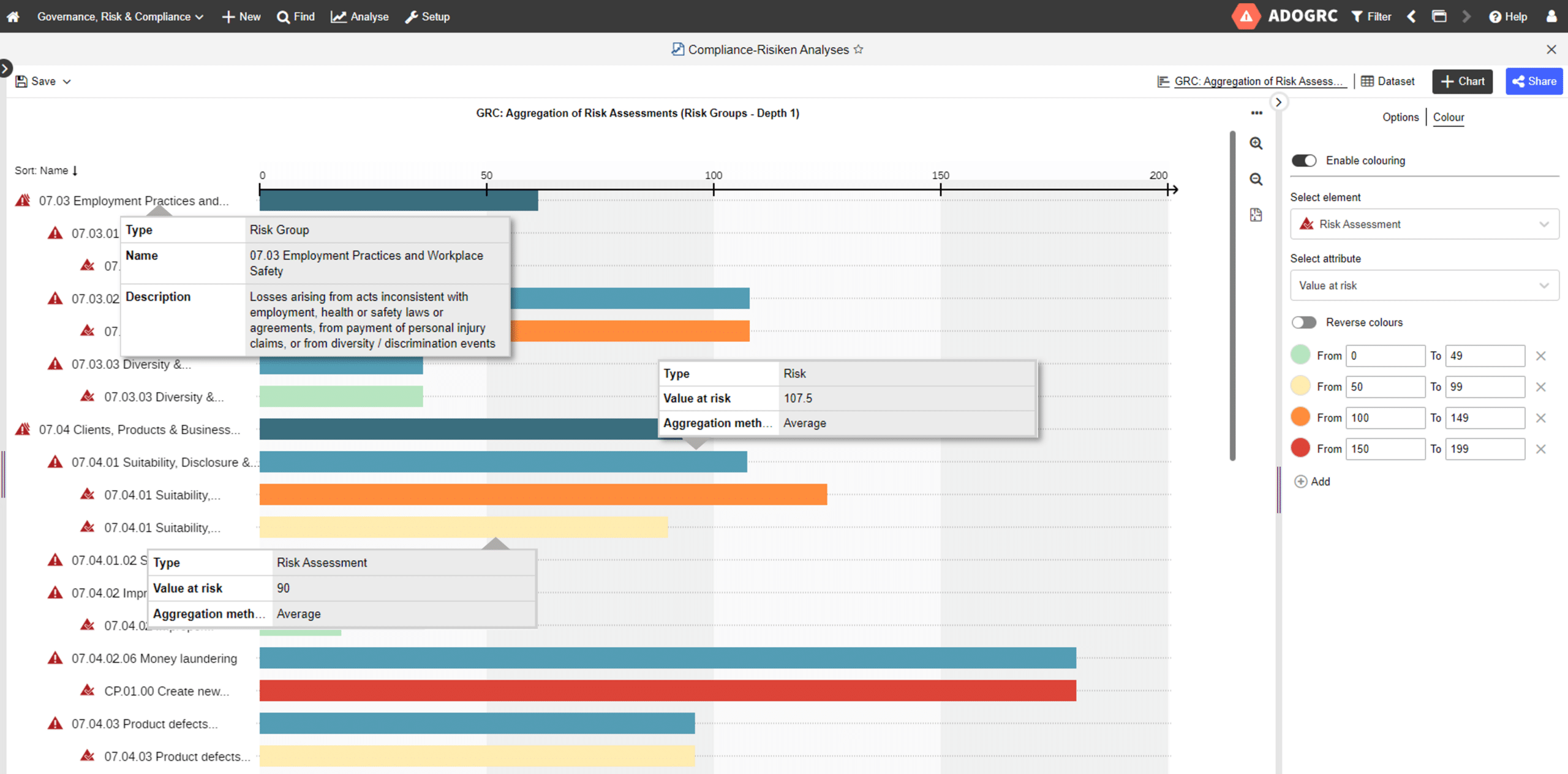
In practice, both legal catalogs and internal documents such as annual reports or audit reports are used to identify compliance risks and obtain an initial overview. This initial overview of all relevant compliance risks should then be validated and expanded through interviews and workshops with the operating units. Ensure that there is accurate and clear documentation of identified risks from the outset. This will reduce future effort and facilitate regular revision of the risk list. With a well-maintained database, it’s also easy to create compelling reports and comprehensive analytics. GRC-Tools such as ADOGRC can be of great help.
Example of a Compliance-Risk Analysis in the GRC suite ADOGRC
Once the list of compliance risks is considered complete for the time being, the next step is to assess them. But more on this in the next section.
Step 2- Implement a compliance risk assessment program
The second step is the assessment of the identified risks. This involves analyzing the compliance risks in terms of their likelihood of occurrence and potential loss. Companies choose between a quantitative and a qualitative risk assessment.
Quantitative Risk Assessment
The quantitative assessment determines the potential loss in euros and estimates the probability of occurrence for each risk. Typically, the quantitative assessment is performed once without consideration of controls (gross assessment) and once with consideration of controls (net assessment). The quantitative assessment method is also recommended in IDW PS 980, an auditing standard of the Institute of Public Auditors. However, it must be taken into account that the damage caused by compliance violations is often difficult to quantify, especially damage to reputation.
Qualitative Risk Assessment
Qualitative assessment classifies risks according to certain criteria, such as traffic light logic (green, amber and red). It provides a rough assessment of risks and is particularly helpful when quantitative data is difficult to obtain or reputational damage is difficult to estimate.
It is important that compliance risks are assessed at periodic intervals. Because risks can change over time, the probability of occurrence and the amount of damage may need to be adjusted.

Step 3- Compliance risks mitigation
Once compliance risks have been identified and assessed, a clear management strategy should be developed for each identified compliance risk. Should the risk be reduced, accepted, transferred, or avoided?
Then define appropriate initiatives to mitigate the risk and strengthen compliance. Companies often rely on initiatives such as compliance training, policies, internal communication campaigns, or internal controls. First, review what internal controls you already have in place to protect against compliance risks. Go through your existing policies and risk management systems and periodically test how effective and efficient these controls are. This will allow you to build on what you have in place and only need to address any compliance gaps that are uncovered. It is also a good idea to obtain confirmations that controls have been executed. This will ensure that the required controls are properly performed.
Summary
As regulatory requirements continue to increase, effective compliance management has become a critical success factor for organizations. Compliance risks affect every organization, regardless of size or type. Compliance breaches that result in significant financial damage are not uncommon. To be best prepared for such incidents, a careful compliance risk analysis is essential. It is the foundation of a successful compliance program and serves the following purposes:
- Identification of key risks
- Adaptation of the compliance program
- Development of internal control mechanisms
- Appropriate allocation of resources
- Evidence and documentation to mitigate liability
A comprehensive and regular compliance risk analysis is the basis for ensuring that companies not only comply with legal requirements, but also protect their financial stability and reputation. By accurately identifying, periodically assessing, and proactively mitigating compliance risks, organizations lay the foundation for long-term success and sustainable corporate governance.