Found this helpful? Share it with peers.
Introduction
Have you ever heard the term “ESG”? With great certainty! It is currently on everyone’s mind… It’s clear that the sustainability reporting that will be mandatory from 2023 onwards will be the subject of much discussion! The only question that remains is: Is your company already prepared?
No? You don’t know how? And you have not heard of ESG until now? Luckily, you’ve landed here! And don’t worry, in this article you will find all the important info you need to know on this topic for now!
What does Environmental Social Governance mean?
In the course of the last few years, a rethinking within society on environmental and social issues has become increasingly noticeable. Companies are particularly affected by this. Instead of focusing purely on economic profits, they should increasingly move in the direction of holistic sustainable management and commitment. “Sustainable” is already the buzzword of the hour around which everything revolves when it comes to ESG! But what is behind the three letters?
The acronym ESG stands for Environmental, Social and Governance and represents the three fundamental sustainability-related areas of responsibility of companies. With these so-called ESG criteria, it will be possible in the future to evaluate and map the sustainability of a company as well as its contribution to society. Let us first take a brief look at the individual areas of responsibility:
Environmental
The first category of the three ESG criteria focuses on the environmental aspect. More specifically, it is about the reciprocal relationship between business and nature. As you know, your company can have both a positive and a negative impact on the environment through its economic activities. Examples of this would be dealing with climate change, the responsible use of limited resources, reduction of the ecological footprint or even sustainable energy management.
Social
The second category of ESG criteria addresses social issues, such as working conditions and occupational health and safety, respect for human rights and much more.
Governance
The third condition of the ESG criteria is about sustainable and responsible corporate governance. This includes, for example, risk and reputation management, the fight against bribery and corruption or data protection.

Environmental Social Governance (ESG) criteria
When taking a closer look at the ESG criteria, a distinction can also be made between two perspectives. These are the inside-out perspective and the outside-in perspective. The former is about the influences a company has on its environment. The outside-in perspective, on the other hand, refers to the influence of the environment on the company. What they have in common is that they deal with the risks and opportunities of a company.
You may ask why this distinction is important? Well, the issue of sustainability is of course not only about how your company is affected but also about what you do for society. This leads us to the all-important question…
Why is Environmental Social Governance important?
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) is crucial for businesses due to its comprehensive approach to sustainability and ethical impact. ESG criteria evaluate how companies perform in areas that are critical for long-term success and societal well-being.
Risk Management:
ESG practices help identify and mitigate risks related to environmental impacts, social responsibilities, and governance practices. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of regulatory fines, legal issues, and reputational damage.
Investor Attraction:
Investors increasingly prioritize ESG criteria when making investment decisions. Companies with strong ESG practices are more attractive to socially responsible investors and can access capital more easily.
Regulatory Compliance:
Adhering to ESG standards ensures compliance with evolving regulations and policies aimed at promoting sustainable and ethical business practices. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Operational Efficiency:
Implementing ESG practices often leads to improved operational efficiency through resource conservation, waste reduction, and better workforce management. This results in cost savings and enhanced productivity.
Long-Term Value Creation:
ESG initiatives contribute to long-term value creation by fostering innovation, operational efficiency, and resilience against market fluctuations. Sustainable practices ensure that the business can thrive in a rapidly changing global environment.
Competitive Advantage:
Companies that excel in ESG practices often gain a competitive edge by building trust and loyalty among consumers, employees, and other stakeholders. Strong ESG performance can enhance brand reputation, customer satisfaction, and employee retention.
ESG is important because it drives sustainable business practices, enhances risk management, attracts investment, ensures regulatory compliance, provides a competitive advantage, and supports long-term value creation.
Environmental social governance examples
ESG is more than just a theoretical concept—many companies have already implemented successful ESG initiatives. Here are some prominent examples:
Environmental
- Carbon Footprint Reduction (Microsoft): Microsoft has committed to becoming carbon-negative by 2030. They are investing in renewable energy and new technologies to remove more carbon than they emit.
- Sustainable Resource Management (Unilever): Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan aims to reduce waste, improve water usage, and source raw materials sustainably across its supply chain.
- Pollution Control (Tesla): Tesla promotes sustainable energy solutions and electric vehicles to reduce air pollution and dependence on fossil fuels.
Social
- Employee Welfare (Google): Google offers extensive benefits like healthcare, flexible working conditions, and career development programs to improve employee satisfaction.
- Community Engagement (Starbucks): Starbucks supports local communities through programs that focus on education, emergency relief, and sustainability efforts.
- Diversity and Inclusion (IBM): IBM has long been a leader in diversity and inclusion, implementing policies and programs that foster a diverse and inclusive workforce.
Governance
- Ethical Leadership (Johnson & Johnson): Johnson & Johnson demonstrates strong governance practices with an independent board and stringent compliance standards.
- Board Diversity (Microsoft): Microsoft prioritizes diversity at the board level, ensuring varied perspectives in decision-making.
- Transparent Reporting (Coca-Cola): Coca-Cola maintains transparency in its financial reporting, helping to ensure stakeholder trust.
Why is Environmental Social Governance in the spotlight right now?
As sustainability reporting becomes more commonplace, especially in Europe, ESG has never been more relevant. The European Union’s mandatory sustainability reporting, effective from 2023, is a clear indication that businesses must integrate ESG into their corporate strategies.
The regulations state that companies meeting certain size criteria—such as having 250 employees or a €40 million turnover—are required to disclose sustainability reports. These reports will be subject to external audits, ensuring transparency and minimizing the risk of greenwashing (when companies misrepresent their environmental efforts).
ESG: How to prepare for the mandatory sustainability reporting
The Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC) system is a fundamental component of corporate governance. Various management functions such as risk management, compliance management or the internal control system serve to protect the company from risks and at the same time to seize opportunities. In order to fulfil these tasks effectively and efficiently, however, an integrated management system is required (check out our webinar on the topic of integrated GRC systems). The 3-lines model has proven itself as a basis for this structure (learn more on the 3-lines model in this blog post). It divides an organization into three lines that define the tasks for the operational units, the GRC functions and the monitoring.
Recently, it has become increasingly clear that the topic of ESG is also establishing itself as a management system or governance function in its own right and can thus be classified as part of the three lines model on the 2nd line with active support from the 1st line.
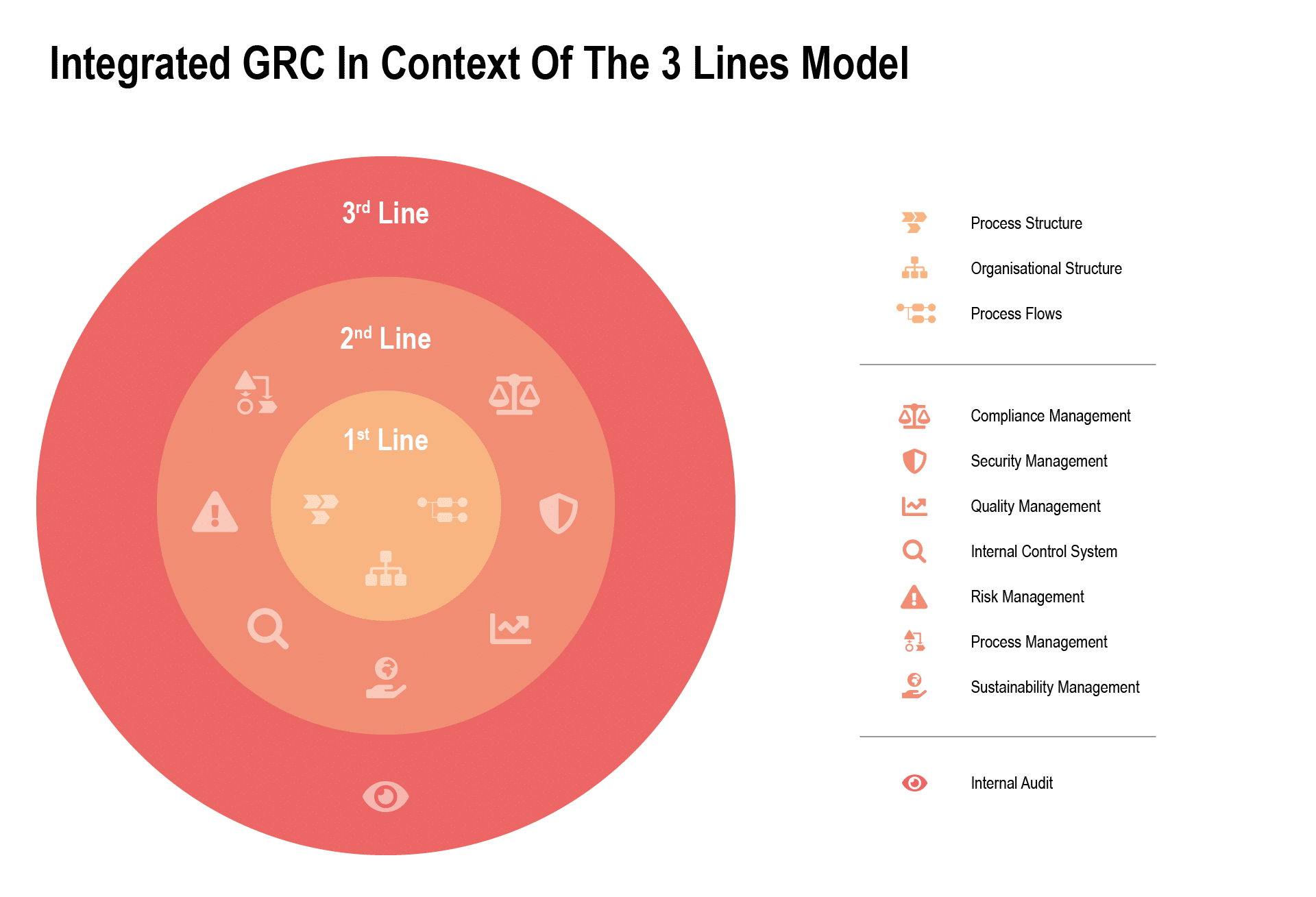
Sustainability as a separate management system in the 3-Lines Model
Summary
ESG goes beyond mere compliance and requires a holistic strategy. Companies that address ESG early on and implement an integrated Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC) system can not only meet the reporting requirements, but also reap the long-term benefits that sustainable business practices offer. The upcoming mandatory sustainability reporting starting in 2023 presents a challenge, but at the same time an opportunity to steer your own company towards a sustainable future.
Ultimately, ESG stands not only for responsibility towards the environment and society, but also for long-term corporate success and competitiveness in an ever-changing business world. Companies that proactively address this change are well equipped to shape a sustainable future.
Referenced papers
Scherer, J. , (N.A.). Nachhaltigkeits- (ESG-/CSR-) Compliance- und -Risikomanagement – die wesentlichen Pfeiler, auch für Resilienz.
Scherer, J., Romeike, F., Grötsch A., (N.A.). Unternehmensführung 4.0: CSR/ESG, GRC & Digitalisierung integrieren.
Scherer J., Grötsch A., (N.A.). (Kombi-) Zertifizierung von Compliance-Risiko-Managementsystemen und Komponenten von Nachhaltigkeits- (ESG-) Berichten.






