Introduction
Imagine implementing a new business process only to discover that it falls short of your expectations. Unforeseen deviations arise, task processing times exceed estimations as a result, and queues build up – all leading to pressure-induced shortcuts and dissatisfied customers due to long waiting times. To tackle and prevent such issues, understanding the actual happenings during process execution becomes paramount. This is where process monitoring comes into play.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of process monitoring, exploring its purpose, benefits, and how it empowers organizations to gain invaluable insights and improve their operations for enhanced efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What is process monitoring?
Process monitoring encompasses a range of activities aimed at improving the operational efficiency by tracking, analysing, and evaluating key processes within an organization.
The extent to which it is then operationalized depends on the level of BPM maturity in the organization.
In organizations with low BPM maturity, process monitoring may be limited or even nonexistent. However, while the organization may lack standardized processes, clear process documentation, or a structured approach to process improvement, process monitoring can still have its benefits, even in this context. For example, by identifying issues in processes, corrective action can be taken and the impact on operations and compliance minimized. By tracking performance, even in a rudimentary way, companies can still identify performance gaps and take targeted initiatives to cover them.
Over time, as an organization’s BPM maturity increases, the ability to effectively monitor processes improves. With well-defined processes, established performance metrics, and process documentation in place, organizations can collect relevant data and measure key performance indicators more accurately. They can also leverage advanced process monitoring techniques and tools to gain deeper insights into process performance.
A higher BPM maturity level enables organizations to integrate process monitoring seamlessly into their overall process improvement initiatives. Eventually, it becomes an integral part of the organization’s culture, with continuous monitoring and analysis ingrained in daily operations. The organization can proactively identify process bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement, driving ongoing process optimization and achieving higher levels of operational excellence.
Process monitoring in the context of the Process Management Life Cycle (PMLC)
Process monitoring is a central element in the Process Management Life Cycle (PMLC). The PMLC is a framework that describes the stages of process development – from the initial discovery of a need for change, to the final implementation and ongoing monitoring of the process. It’s typically applied on released to-be processes. Hence, process monitoring falls into the final phase of the Process Management Life Cycle, the Feedback & Controlling phase.
To learn more about the PMLC framework, check out our blog post on Business Process Management. Or read up on our Process Documentation, Process Analysis or Process Implementation blog posts for deeper insights into these phases.
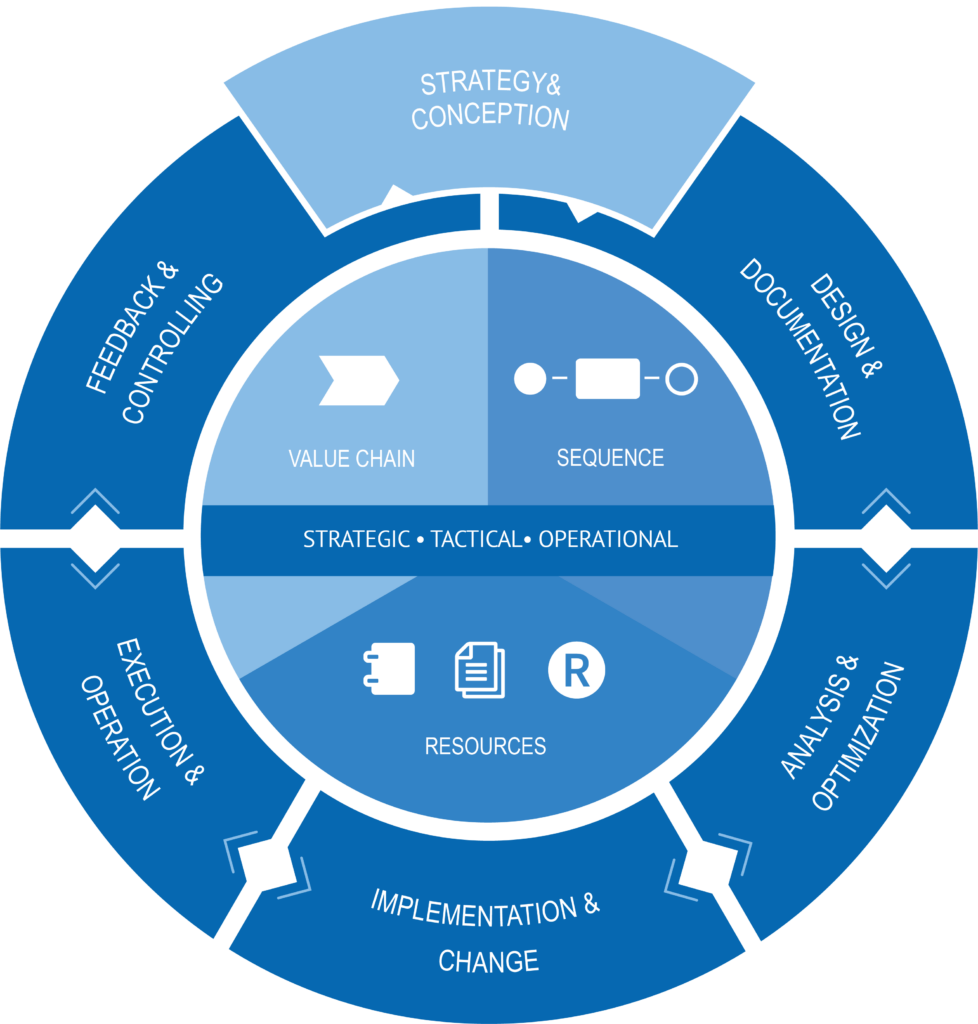
BOC Group’s Process Management Lifecycle (PMLC)
What are the important aspects of process monitoring?
Critical metrics form the backbone of business process monitoring. Organizations define and track key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with their strategic objectives and operational priorities. These KPIs can vary depending on the nature of the processes being monitored and the specific goals of the organization. For instance, a manufacturing company may focus on metrics such as cycle time, production yield, defect rate, and equipment utilization, while a customer service-oriented business may emphasize metrics like average response time, customer satisfaction scores, and first-call resolution rate.
By continuously monitoring and measuring these metrics, organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of their processes’ performance. They can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in the data, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and take appropriate actions accordingly. For example, if a particular process consistently exceeds its defined cycle time, stakeholders can investigate the underlying causes, such as resource constraints or inefficient task sequences, and implement corrective measures to optimize the process flow. To successfully and efficiently monitor your KPIs, we recommend relying on tool-based support, such as our ADONIS Strategy & Performance Management.
Why is process monitoring important?
Business process monitoring brings various benefits to organizations that drive operational excellence and organizational success.
Improved efficiency
Process monitoring identifies bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Analysing real-time data streamlines workflows, optimizes resource allocation, and eliminates non-value-added activities. This boosts process efficiency, reduces cycle times, and enhances productivity, maximizing resource utilization.
Enhanced product or service quality
Process monitoring ensures quality by tracking performance indicators and gathering customer feedback. It enables prompt corrective actions, quality control measures, and consistent delivery of high-quality products/services, fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Better risk management
Process monitoring identifies and mitigates risks by continuously tracking metrics and indicators. Early detection enables proactive intervention, minimizing impact on operations, reputation, and compliance. It enhances risk management, organizational resilience, and regulatory compliance.
Increased agility
Process monitoring offers real-time insights into process performance, enabling organizations to adapt, make informed decisions, and respond swiftly to evolving business conditions. Embracing process monitoring enhances agility, seizes opportunities, and maintains a competitive edge in dynamic markets.
Cost savings
Process monitoring identifies potential bottlenecks and unnecessary costs. By analysing key performance metrics, organizations spot underutilized resources, duplicated tasks, and error-prone processes. This knowledge drives process improvements, automation, and resource reallocation for cost savings. Optimized processes reduce waste and boost cost efficiencies, improving the bottom line.
Soft benefits, process improvement over time, and more
Process monitoring not only delivers quantifiable benefits but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. It enables iterative enhancements, collaboration, transparency, and accountability. Insights gained contribute to the organization’s knowledge base, promoting best practices and a learning culture for ongoing process improvement.
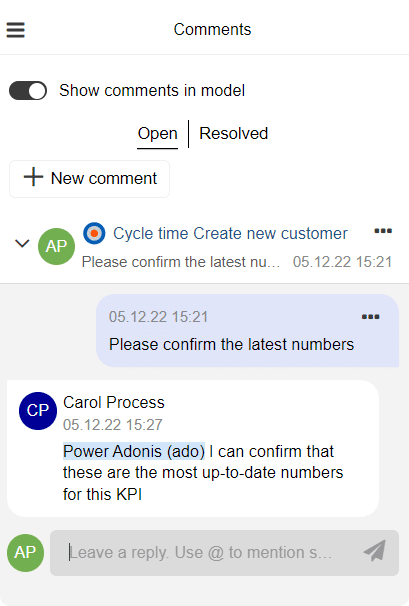
The commenting feature of the ADONIS BPM suite promotes BPM collaboration
Process monitoring techniques
There are different tecniques to implement process monitoring in your organization. Each type of process monitoring offers a unique perspective and set of tools to track, analyse, and optimize different dimensions of business processes. By understanding these diverse monitoring approaches, organizations can gain valuable insights into their processes, identify areas for improvement, and drive continuous innovation.
Functional Monitoring
Functional monitoring tracks and evaluates performance and adherence to functional requirements in a business process. It ensures data validation, rule enforcement, system integrations, and policy compliance. By continuously monitoring these aspects, organizations maintain process correctness, data integrity, and desired outcomes. Functional monitoring offers insights into process health and effectiveness, allowing prompt issue identification and resolution.
Technical Business Process Monitoring
Technical business process monitoring oversees the technical infrastructure and components supporting process execution. It tracks system availability, response times, resource utilization, and error rates. This enables identification of performance bottlenecks, system failures, or resource constraints that affect process efficiency and reliability. By proactively managing the technical infrastructure, optimizing resources, and ensuring smooth process execution, organizations benefit from technical business process monitoring.
Process Mining
Process mining is an advanced form of process monitoring that uses data analysis to uncover insights from event logs. It visualizes actual process flows, deviations, patterns, and inefficiencies. Process mining identifies compliance issues and variations from intended process models. By integrating real-time and historical data, it facilitates process analysis, optimization, and redesign, promoting continuous improvement and operational excellence. For more information on process mining and how we implement it with our BPM tool ADONIS.
Steps for successful process monitoring
To effectively monitor and optimize business processes, organizations need to operationalize a systematic approach that involves several key process monitoring steps. This ensures that the monitoring efforts align with the objectives of the processes being analysed and provide actionable insights for improvement. In this section, we will explore the process of operationalizing process monitoring and delve into the sequential steps.
1. Define Process Objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Operationalizing process monitoring requires clear direction. Define process objectives, desired outcomes, and performance levels. Choose specific, measurable, relevant KPIs aligned with these objectives. This foundation guides a successful monitoring strategy, illuminating the path to success.
2. Establish Data Collection Mechanisms
Robust data collection is essential for effective process monitoring. Identify relevant data sources, including transactional systems, IoT devices, and sensors. Implement structured and consistent data collection mechanisms, leveraging automation and integration for accuracy and reliability. These foundations ensure comprehensive and reliable process monitoring.
3. Implement Real-Time Data Analytics
Real-time data analytics are essential for process monitoring. Capture and analyse data in real or near real-time. Utilize analytics tools like BI platforms, process mining software, or custom solutions to transform data into actionable insights. Apply statistical analysis, data visualization, and other techniques for meaningful outcomes.
Real-time data analytics in ADONIS
4. Develop Monitoring Dashboards
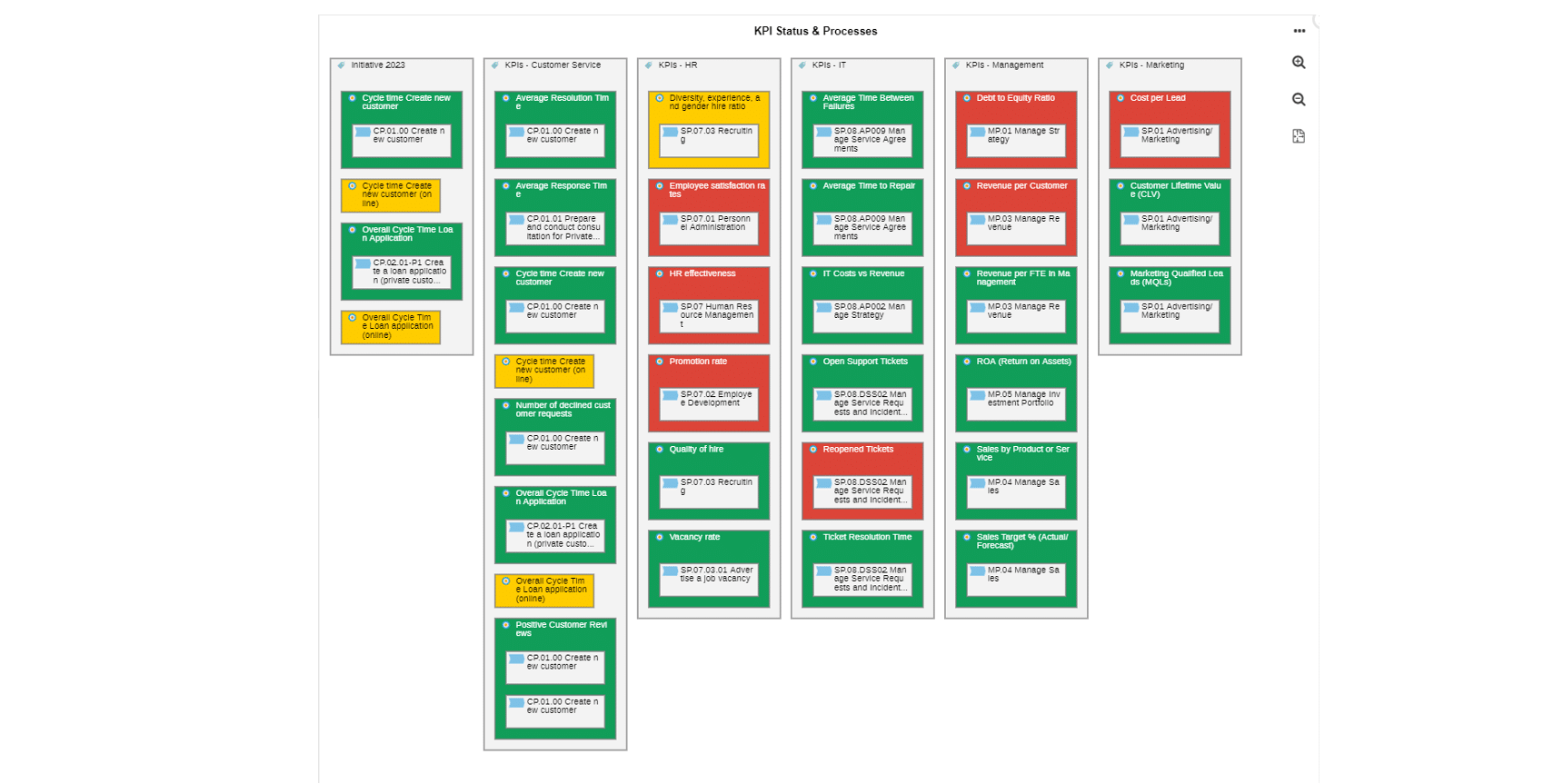
Create dynamic, real-time monitoring dashboards for stakeholders. Display relevant KPIs, metrics, and trends in a clear and intuitive manner. Use charts, graphs, and visuals for easy interpretation. Customize dashboards to meet stakeholder needs. Empower stakeholders to make informed decisions and drive process optimization.
5. Set Thresholds and Alerts
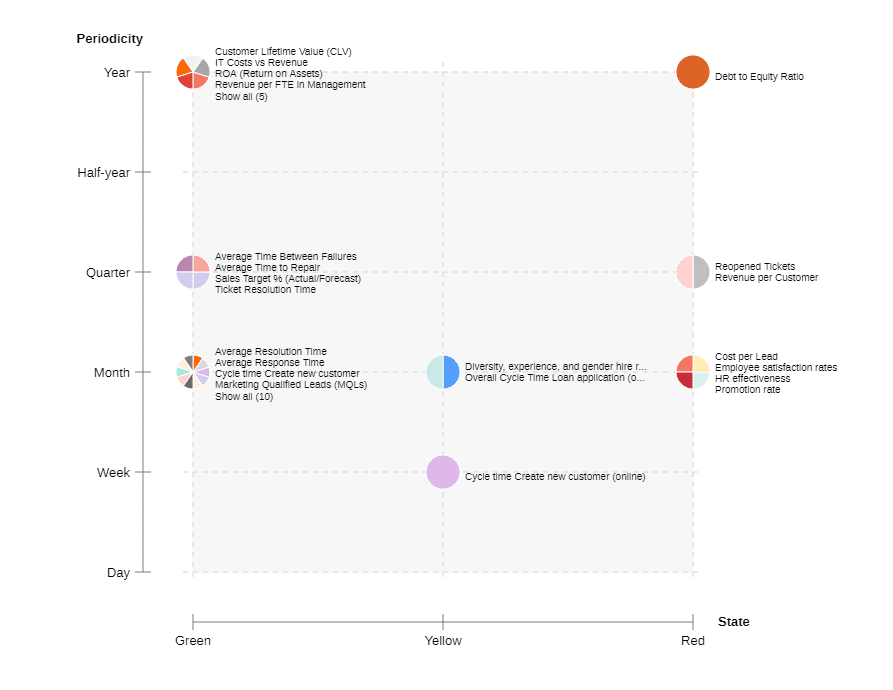
To effectively monitor a process, it is important to establish performance thresholds for the KPIs being tracked. These thresholds define the acceptable ranges for the metrics and indicate when a performance deviation requires attention. Implement alert mechanisms that notify stakeholders when a KPI exceeds the defined thresholds or when predefined events or anomalies occur.
An example of a KPI Monitoring dashboard incl. thresholds in the BPM suite ADONIS
6. Establish Governance and Ownership
Establish clear governance and ownership for effective process monitoring. Define roles and responsibilities of stakeholders. Assign accountability for data accuracy and quality. Review and update governance framework regularly to adapt to business needs and process requirements.
7. Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Iteratively review monitored data, analyse insights, and identify improvements. Optimize the process based on said findings. Redesign, automate, or reallocate resources as needed. Regularly assess and adjust the monitoring strategy to align with changing business objectives.
Hint: Get our Process Monitoring Steps Poster for takeaway.
Process monitoring benefits
Process monitoring plays a pivotal role in Business Process Management (BPM), offering numerous advantages that contribute to organizational success. Here are the key benefits:
Improved Efficiency:
Process monitoring enables organizations to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, resulting in streamlined workflows and increased overall efficiency.
Cost Efficiency:
A tangible benefit of effective business process management is cost efficiency. Process monitoring helps identify areas for cost reduction and revenue increase.
Proactive Problem Resolution:
Process monitoring allows organizations to proactively identify and address issues, preventing potential disruptions and enhancing overall operational stability.
Strategic Alignment:
Tighter, strategically aligned process controls result from process monitoring, ensuring that business processes are in harmony with organizational goals.
Enhanced Agility and Scalability:
Greater business agility and scalability are achieved through well-monitored processes, allowing organizations to adapt swiftly to changing market conditions.
Summary
In conclusion, business process monitoring empowers organizations to unlock hidden potentials, achieve operational excellence, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. It provides stakeholders with valuable insights into their processes, enabling them to identify areas for improvement, drive efficiency, reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and foster innovation. By adopting a systematic and data-driven approach to process monitoring, organizations can optimize their operations, adapt to changing market dynamics, and navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape with confidence.
If you want to get the most out of process monitoring, make sure you have the right tools to get the job done. Get to know our customers’ favorite ADONIS and its free BPM Suite and find out how you can leverage it to monitor your business processes.
To gain a more comprehensive understanding of process monitoring, be sure to check out our related resources provided below. Don’t miss out on what we have to offer and give your business the boost it needs!
Browse related BPM content
Sources:
1 – Appian. (n.d.). Business Process Monitoring: The Key to Success. Retrieved from https://appian.com/blog/acp/process-mining/business-process-monitoring-success.html
2 – cFlow. (n.d.). Business Process Monitoring: Everything You Need to Know. Retrieved from https://www.cflowapps.com/business-process-monitoring/
3 – Dumas, M., La Rosa, M., Mendling, J., & A Reijers, H. (2013). Fundamentals of business process management. Springer.
4 -Kissflow. (n.d.). Business Process Monitoring: Streamlining Your Processes for Better Efficiency. Retrieved from https://kissflow.com/workflow/bpm/business-process-monitoring-streamline-processes/
5 – Predictive Analytics Today. (n.d.). What is Business Process Monitoring? Retrieved from https://www.predictiveanalyticstoday.com/what-is-business-process-monitoring/