Found this helpful? Share it with peers.
Introduction
The NIS2 Directive (Directive (EU) 2022/2555) marks a major shift in European cybersecurity governance. For many organizations, it represents more than a regulatory update: it requires a structural change in how cybersecurity is managed, overseen, and continuously improved.
Rather than merely introducing new technical measures, NIS2 elevates cybersecurity to a strategic, governance-level responsibility, placing clear expectations on leadership and embedding resilience across the entire organization.
This article focuses on what NIS2 compliance means in practice and how to build a scalable, audit-ready cybersecurity framework aligned with the directive’s requirements.
For an introductory overview of the directive itself, affected sectors, and key components, see our main NIS2 overview page.
What NIS2 Compliance Really Means
Compliance with NIS2 goes far beyond implementing isolated controls. It involves building an integrated governance system that spans:
-
Clear management accountability
-
Risk-based security management and prioritization
-
Structured incident reporting and response workflows
-
Business continuity and resilience planning
-
Supply-chain and third-party security oversight
-
Documentation, evidence, and cooperation with supervisory authorities
In short, NIS2 requires organizations to demonstrate not only that they have controls in place, but that those controls are managed, monitored, and continually improved.
This shift challenges organizations to move from ad-hoc cybersecurity practices to a repeatable, measurable, and transparent governance model.
NIS2 vs NIS1: What Has Changed?
Organizations familiar with the original NIS Directive will find that NIS2 introduces substantial changes in scope, accountability, enforcement, and operational expectations. These differences include:
-
A broader set of in-scope sectors
-
Standardized size-cap criteria for inclusion
-
Explicit top-management accountability
-
Detailed requirements for risk management, incident handling, and supply-chain security
-
A multi-step incident reporting process
-
Stronger and more harmonized supervision
-
Significantly higher sanctions
These changes elevate cybersecurity from an operational concern to an enterprise-level governance priority—and make structured frameworks essential.
| NIS1 | NIS 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Scope & Sectors | Limited to a small set of essential service operators and a few digital service providers. | Expanded to many more essential and important entities across additional sectors (e.g., manufacturing, food, waste, digital infrastructure). |
| Size Criterion | No standardized size-based criteria; inclusion mainly depended on sector-specific designation. | Applies to all medium and large entities of sectors in scope through size-cap rule – with additional inclusion of smaller entities for certain high-impact services. |
| Governance & Management | Operational security focus with limited management obligations. | Explicit board-level responsibility, mandatory oversight, and cybersecurity training for management bodies. |
| Risk Management Duties | General requirement for “appropriate and proportionate” security measures. | Detailed set of required technical and organizational measures (e.g., risk analysis, incident handling, BCM, supply-chain security, encryption). |
| Incident Reporting | Single reporting step within 72 hours for significant incidents. | Three-step reporting for significant incidents: early warning (24h), incident notification (72h), and final report (1 month). |
| Supervision & Sanctions | Less harmonized national supervision and lower sanctions. | Stronger, harmonized oversight and significantly higher fines (up to €10M or 2% of global turnover). |
| Supply-Chain Security | Only indirectly addressed. | Explicit obligations to assess and control ICT supply-chain and third-party risks. |
Overview of the key differences between NIS1 and NIS2
Key NIS2 Requirements (and What They Mean in Practice)
NIS2 introduces a series of far-reaching security, governance, and operational requirements that apply to in-scope essential and important entities. The following are the core requirements areas and how they typically translate into organizational responsibilities in practice.
1. Governance & Accountability
NIS2 introduces explicit obligations for the management body, including oversight, resource allocation, and mandatory participation in cybersecurity training.
Organizations must ensure leadership can:
-
Approve and supervise cybersecurity risk management
-
Monitor controls and mitigation activities
-
Demonstrate compliance through documentation and evidence
-
Take responsibility for deficiencies
How ADOGRC helps:
A unified governance structure linking responsibilities, controls, risks, and KPIs gives management real-time visibility and auditable evidence at all times.
2. Risk Management
NIS2 requires a risk-based approach to security. This includes:
Maintaining asset registers and criticality mapping
Conducting structured cyber and operational risk assessments
Implementing, monitoring, and reviewing technical and organizational measures
Tracking mitigation and treatment plans
How ADOGRC helps:
Centralized risk repositories, automated workflows, and linked controls streamline assessments and ensure consistent, evidence-based risk management.
3. Incident Management & Reporting
NIS2 mandates a three-step reporting structure:
-
Early warning within 24 hours
-
Incident notification within 72 hours
-
Final report within one month
To comply, organizations must have:
-
Defined classification criteria
-
Clear response processes and responsibilities
-
Complete incident documentation and evidence trails
How ADOGRC helps:
End-to-end incident lifecycle management ensures every incident is tracked, analyzed, linked to controls, and reportable in accordance with NIS2 timelines.
4. Supply-Chain & Third-Party Security
NIS2 significantly strengthens expectations for supplier and service-provider oversight. Organizations must:
-
Identify and document critical dependencies
-
Assess vendor security posture
-
Enforce contractual security requirements
-
Track third-party risks continuously
How ADOGRC helps:
Supplier assessments, risk scoring, and remediation tracking allow organizations to manage supply-chain exposure within a single integrated platform.
5. Business Continuity & Crisis Management
NIS2 emphasizes resilience through:
-
Business Impact Analyses (BIA)
-
Definition of recovery objectives (MTPD, RTO, RPO)
-
Tested continuity and disaster recovery plans
-
Crisis communication structures
How ADOGRC helps:
Linked continuity plans, BIAs, recovery metrics, and dashboards ensure readiness and compliance across all critical operations.
Hint: Discover ADOGRC’s integrated solution for Business Continuity Management.
6. Compliance Oversight & Supervision
NIS2 differentiates between essential and important entities, with stricter ex-ante and ex-post supervision for essential entities. Therefore organizations must:
- Maintain documentation and evidence of risk management measures.
- Monitor the implementation of measures for full transparency
- Be prepared for audits, inspections, and corrective orders from authorities
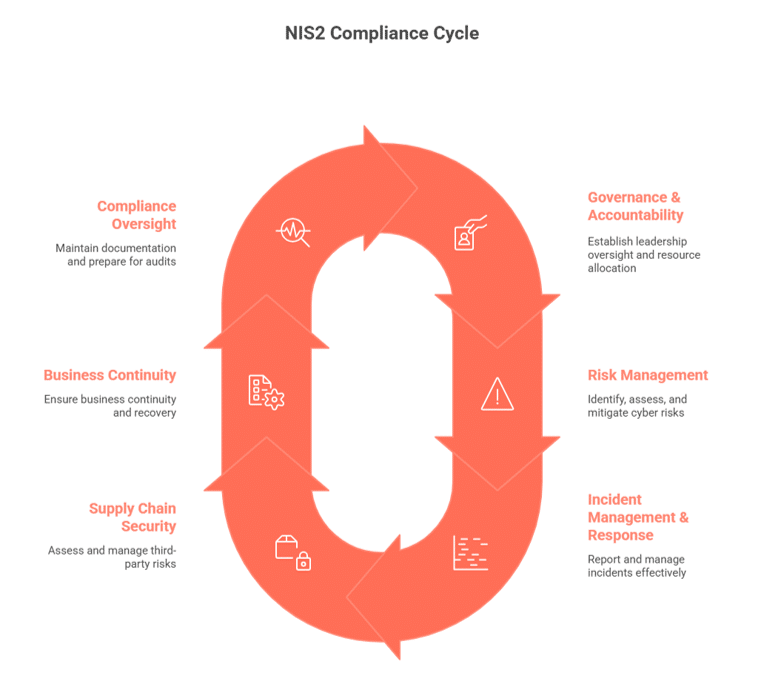
NIS2 requirements visualized in the compliance cycle
Through its compliance library, ADOGRC maps all applicable company-specific requirements to risks, measures, controls and owners. Real-time status dashboards and reports support audits, inspections, and documentation obligations for both essential and important entities.
Simplify your NIS2 compliance with the integrated solution of ADOGRC.
Common Challenges When Implementing NIS2
Even with a well-defined framework, implementing NIS2 can be tougher than expected. Here are typical challenges you may encounter:
-
Fragmented National Execution
Member states implement NIS2 via their own national laws and timelines, which creates uncertainty and variation in details such as sector lists, supervisory practices, and deadlines. -
Limited Resources & Budget
Medium-sized entities and public institutions often lack specialized cyber staff, tools, or budget to build manual governance frameworks. The requirements of NIS2 quickly exceed spreadsheet-based approaches. -
Governance Gaps & Lack of Management Involvement
Many organizations still see security as an IT topic. Since NIS2 shifts responsibility to the board and requires proper training, governance structures and reporting lines need to be revised. -
Supply Chain Complexity & SME Impact
Even organizations not directly in scope will feel NIS2 via contractual requirements from customers. Suppliers must demonstrate controls, incident reporting capabilities, and continuity arrangements to remain part of critical value chains. -
Overlapping Frameworks
NIS2 rarely exists in isolation. Many entities are already working with ISO 27001, DORA (for financial entities), NIST CSF, or BSI IT-Baseline.
Without a central view, organizations risk duplicated work and inconsistent controls.
Instead of rebuilding a framework from scratch, a mapping approach supported by a structured compliance library helps align NIS2 requirements with your existing frameworks. This allows you to identify overlaps, reduce duplication, and manage compliance more easily within your current processes.
5 essential Steps to Achieve NIS2 Compliance
This section outlines a practical, implementable approach to achieving NIS2 readiness.
Step 1: Assess Exposure and Maturity
Identify whether NIS2 applies to your organization, conduct a gap assessment, and review current governance and risk posture.
Step 2: Define Governance, Roles & Controls
Clarify responsibilities, formalize policies, assign owners, and introduce a structured control framework aligned with NIS2.
Step 3: Map NIS2 Requirements to Existing Frameworks
Reuse controls where possible to avoid duplication and strengthen auditability.
Step 4: Implement Continuous Monitoring & Incident Handling
Set up dashboards, KPIs, reporting cycles, and structured incident workflows.
Step 5: Report, Audit & Improve
Maintain complete documentation, run audits, and integrate lessons learned into the security framework.
Turning NIS2 Into an Advantage
While NIS2 brings new obligations, it also offers a clear opportunity to modernize how cybersecurity is governed and operated:
- Improved visibility & ownership – map risks, incidents and controls to accountable stakeholders so everyone knows who is responsible and why.
- Faster response – define processes, playbooks and measurable KPIs to shorten detection and recovery times.
- Stronger trust – customers, partners and regulators gain confidence from a transparent, risk-based approach.
- Aligned risk & resilience — connect cyber risks with enterprise risk management and resilience initiatives so security decisions directly support broader business objectives.
Organizations that embed NIS2 within their broader GRC strategy turn compliance into a strategic differentiator rather than a cost.
Conclusion
NIS2 fundamentally reshapes cybersecurity governance across the EU. Achieving compliance requires a structured, risk-based framework that aligns responsibilities, strengthens incident management, and maintains supply-chain resilience.
Platforms like ADOGRC help organizations operationalize these requirements by connecting risks, controls, incidents, continuity measures, and supplier oversight in one integrated environment, ensuring compliance becomes a driver of resilience and long-term trust.





