Introduction
Getting everyone on the same page is a hard task, especially in the everyday business setting. Think about all the different departments, each with its way of doing things. It’s like speaking different languages within the same company, which often leads to misunderstandings and inefficiencies. This is especially problematic when organizations want to streamline and standardize the way they do business. To add to the complexity, organizations are not homogeneous entities, they need to cooperate, both internally and externally, both locally and internationally. There is a solution that bridges these communication gaps and paves the way for streamlined operations — BPMN. Imagine it as a universal language that transcends departmental barriers, enabling diverse business units to collaborate seamlessly.
This blog post is your guide to unlocking the full potential of BPMN, a tool that transforms these challenges into opportunities. By providing a standardized visual language, BPMN enables you to effectively communicate complex processes, fostering transparency and alignment across your organization. Keep reading to discover how BPMN’s intuitive diagrams not only break down barriers, but also create a solid basis for process optimization.
What is Business Process Modell and Notation (BPMN)?
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) is a graphical notation standard for business process modelling. It is a widely accepted and recognized notation standard used by BPM software tools to create visual representations of business processes. BPMN 2.0 is the most recent version of the BPMN specification, and it offers a comprehensive set of symbols and rules for process modelling.
A brief history of BPMN:
The origin of Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) dates back to the early 2000s when the need for a standardized graphical notation to model and communicate business processes became increasingly apparent. Before BPMN’s development, various organizations and industries used their own proprietary notations, leading to inconsistencies, difficulties in understanding, and barriers to collaboration.
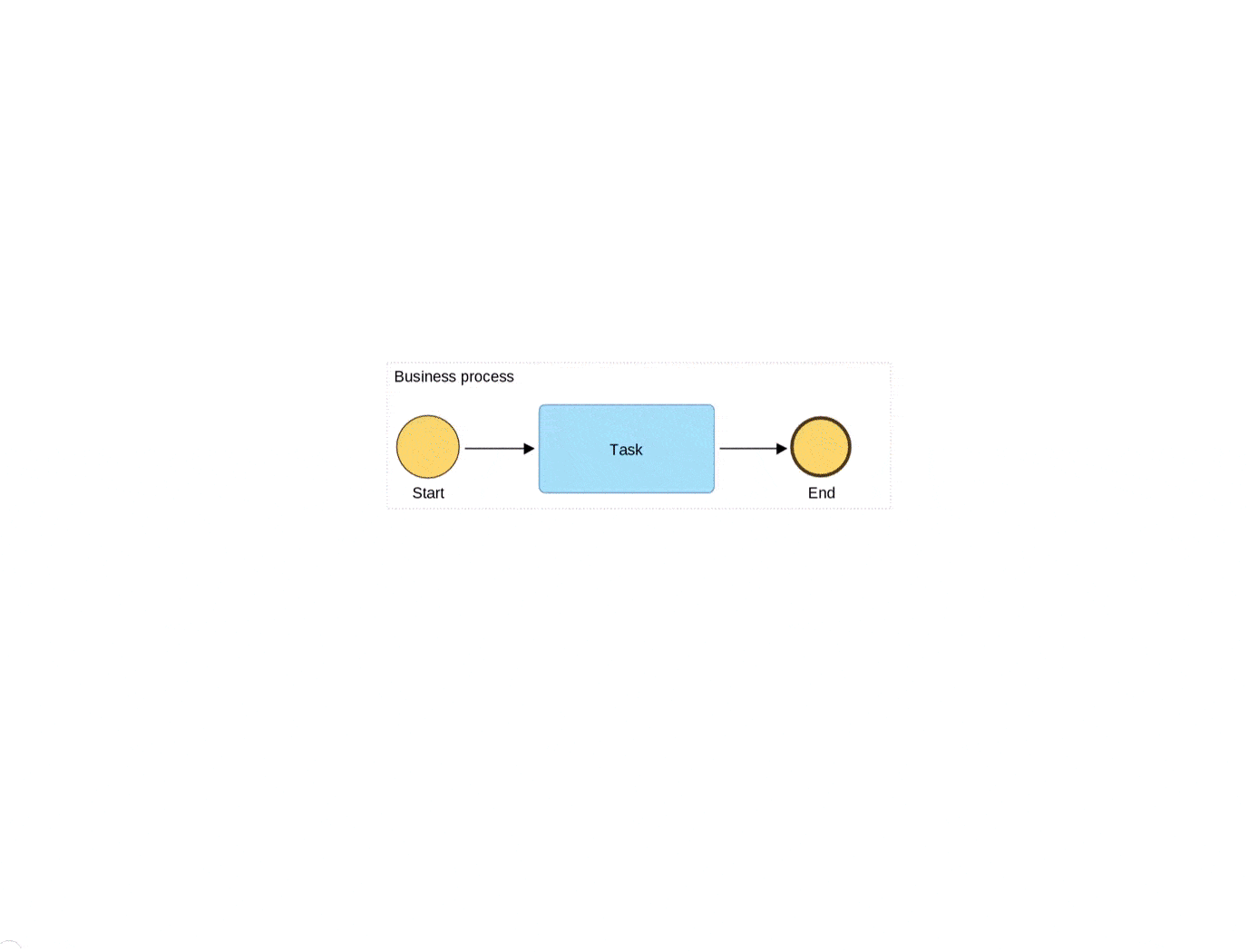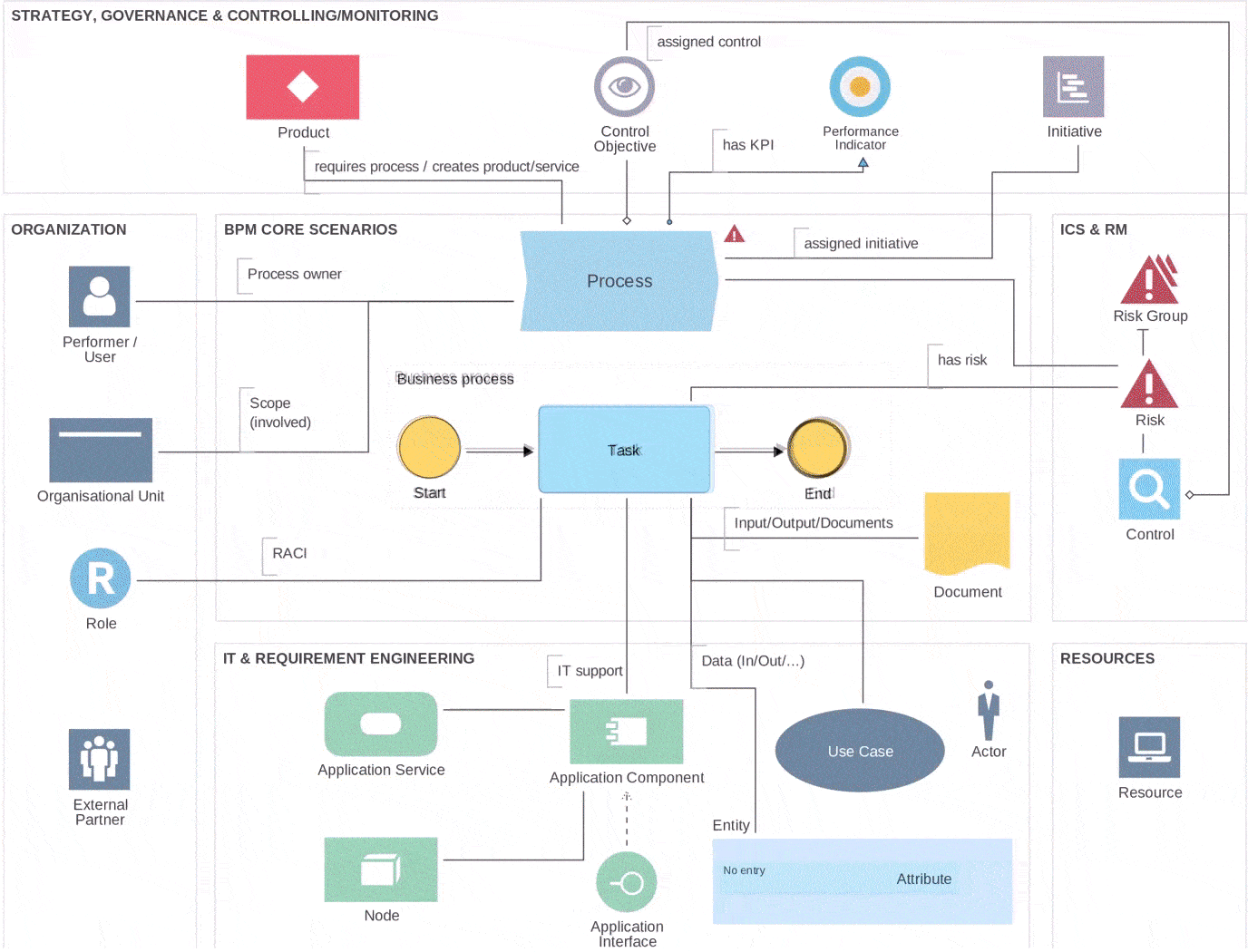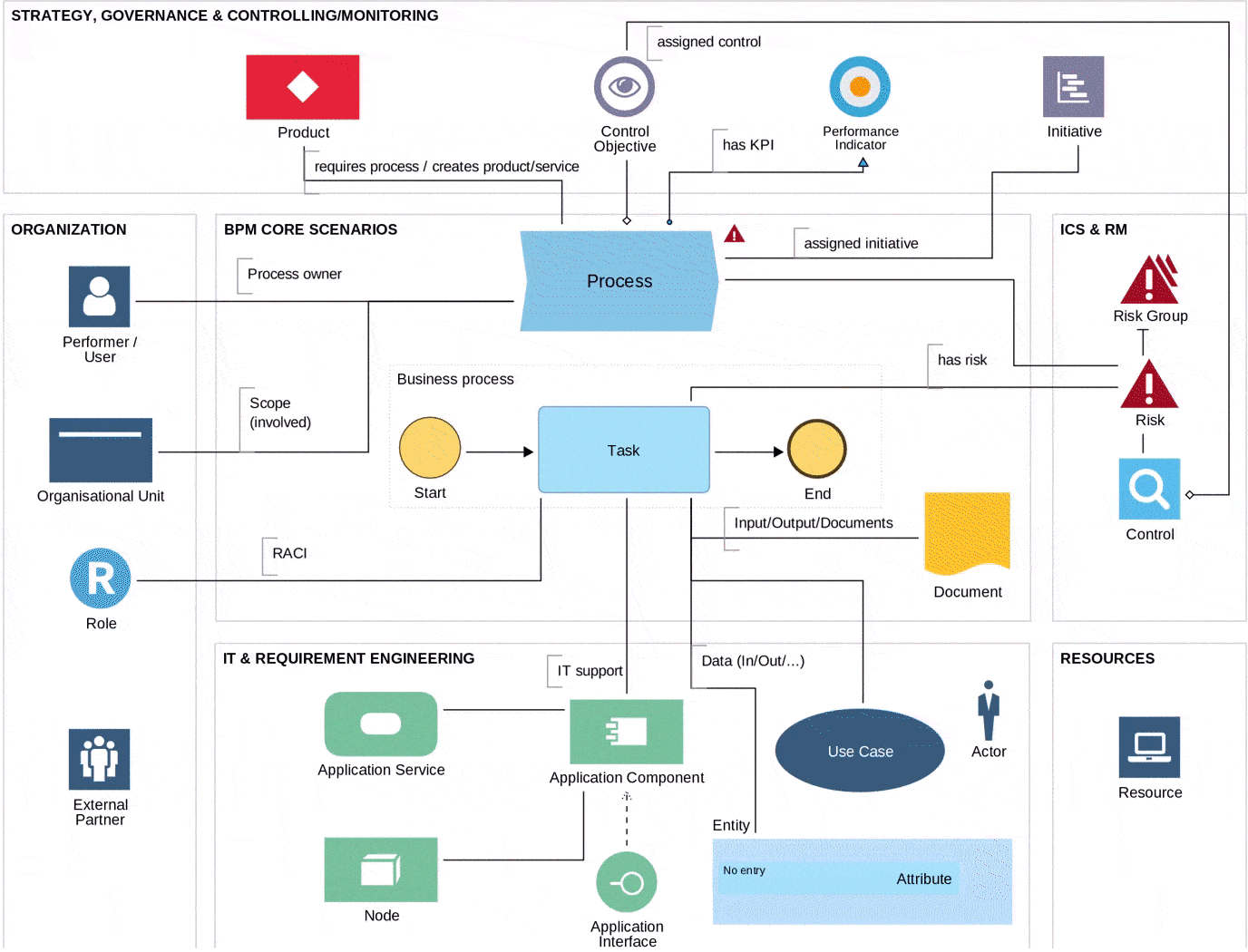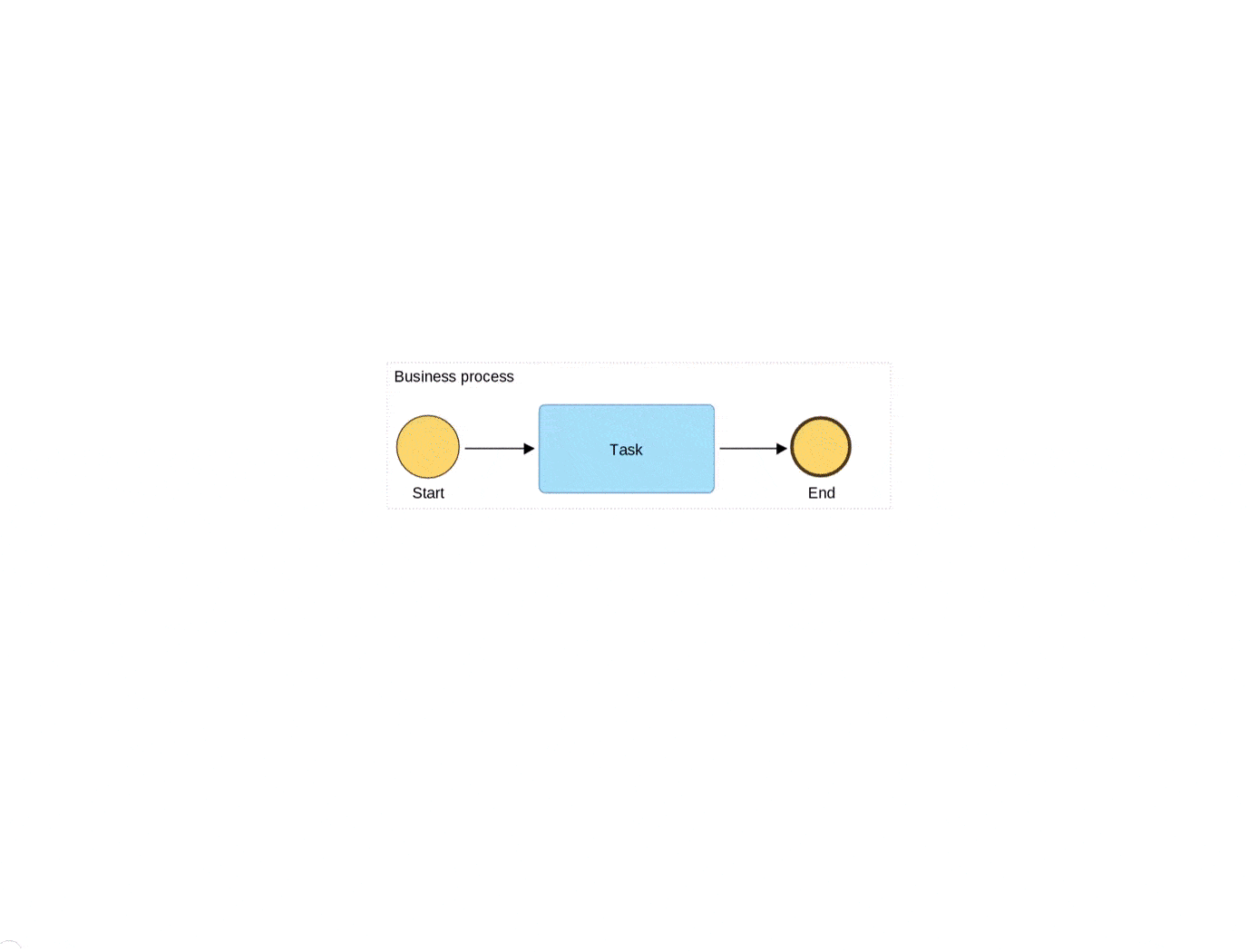
BPMN 2.0 Metamodel
BPMN 2.0 is an intuitive and standardized notation, which enables clear communication among business analysts, process owners, and stakeholders while also facilitating effective collaboration and decision-making throughout the organization. With its rich set of modelling constructs, including activities, events, gateways, flows, and data objects, BPMN 2.0 provides an opportunity to capture all the nuances of complex business processes. The notation allows the modelling of end-to-end processes, as well as individual sub-processes within a larger process.
Embedded at the core of BPMN 2.0 is the metamodel, a foundational aspect that defines relationships and components intrinsic to a business process. This standardized framework is widely adopted in the industry and versatile in its ability to model various categories of business processes, including human workflows, system integrations, and decision-making processes.
The BPMN 2.0 metamodel consists of several key components that make up the notation, including:
Benefits of Using BPMN
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a powerful tool for organizations seeking efficient Process Management. Implementing BPMN provides several advantages to companies:
Comprehensive and Consistent Notation
BPMN offers a unified and consistent notation that covers various aspects of business processes, ensuring clarity and understanding across the organization.
Clear Graphical Language
BPMN utilizes a clear graphical language, making it easy to comprehend compared to traditional text-based descriptions, enhancing communication and understanding within the organization.
Business-Friendly Concepts
BPMN includes constructs easily understandable to business stakeholders, such as “start events” and “end events,” making it accessible to a broader audience, including non-technical users.
Comprehensive and Consistent Notation
BPMN offers a comprehensive and consistent notation that covers various aspects of business processes, ensuring uniformity and clarity in process documentation and communication.
Tool Neutrality
Being a neutral notation adopted by many solutions providers, BPMN allows organizations to choose from multiple tools available, providing flexibility and adaptability.
Simplified Process Mapping
BPMN simplifies the mapping of business processes, making it more accessible to a broader audience, including non-technical stakeholders.
Support for Business Process Modeling/Analysis:
BPMN tends to be favored by those with a business process modeling/business analysis background, making it a suitable choice for organizations focusing on these areas.
Standardization of Processes:
Companies benefit from the standardization of processes through the use of BPMN, leading to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and better overall process management.
Scalable Flow Charts
BPMN’s flexibility allows the creation of flow charts that can be as simple or as complex as needed, accommodating the diverse needs of different processes within an organization.
Implementing BPMN empowers organizations with a standardized, business-friendly approach to process modelling, fostering transparency, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Different types of BPMN diagrams
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) encompasses several diagram types, each serving a specific purpose in visualizing and documenting business processes. Here are the key BPMN diagram types
Process Diagrams
These diagrams provide a detailed representation of the sequential flow of activities within a single process. They use symbols such as tasks, gateways, and events to illustrate the process flow.
Collaboration Diagrams
Collaboration diagrams show how different process participants interact with one another. They highlight the flow of messages and events exchanged between various entities involved in a collaborative business process.
Choreography Diagrams
Choreography diagrams focus on the interaction between two or more participants without specifying the internal details of each participant’s process. They illustrate the sequence of messages and activities exchanged among participants.
Conversation Diagrams
Conversation diagrams provide an overview of how participants communicate and collaborate in a business process. They showcase the relationships and interactions between different participants without delving into the detailed process flow.
Data Diagrams
Data diagrams focus on the information exchanged within a business process. They represent data objects, artifacts, and data associations, providing insights into the flow and transformation of data within the process.
Understanding these BPMN diagram types enables organizations to comprehensively model and analyze their business processes, fostering clarity and effective communication.
BPMN 2.0 metamodel key components
These are the building blocks of a BPMN diagram and include activities, events, and gateways. Activities represent work to be done, events represent triggers or results, and gateways represent decision points.
Data Objects
Represent the flow of information in a business process, information contained in documents, emails, letters etc. They can be used in a process or come as an outcome of the process.
Connecting Objects
These include sequence flows, message flows, and (data) associations. Sequence flows define the order of activities, message flows represent information exchange, and associations provide additional information and annotations to the diagram.
Swimlanes
These represent the participants or groups involved in the process. Swimlanes can be organized into pools and lanes, which help to clarify roles and responsibilities.
Artifacts
These are additional elements that can be used to provide additional information or details about the process. Artifacts can include annotations, data objects, and groups.
Overall, the BPMN 2.0 metamodel provides a standardized way to model and communicate business processes in a clear and consistent way. By using a common notation, different stakeholders can easily understand and analyze the process, making it easier to identify areas for improvement and how to optimize processes.
Practical implications of BPMN 2.0
BPMN is all about the process, which embodies a series of organized activities dedicated to achieving a goal or an objective of the organization. These series of steps start with an event and end in one. Between these events there are tasks following each other, traced with sequence flows. Occasionally, there are some decision points in the process, which are marked by gateways that split the process and later bring the flow back together. Business processes always involve coordinating individuals, resources, and/or technologies. These components (artifacts) within a business process should be also defined, though sometimes their complexity can lack practicality in day-to-day business applications.
The ultimate goal is to use the notation to clearly communicate and document processes in a way that is easily understood by all stakeholders involved. Therefore, it is crucial to adapt the notation to fit the specific needs of a business. This means that organizations may need to customize the notation by adding or removing elements, or by simplifying certain components to make the notation more practical for everyday use. By doing so, organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize their processes, leading to improved efficiency and effectiveness.
ADONIS Metamodel extends the BPMN to fit modern business needs
BPMN Fit for Business
Another way to make BPMN fit to your business needs, is to enhance the metamodel with concepts and attributes that are relevant to mapping professional application scenarios. Additionally, organizations may choose to add other modelling languages for specific uses, such as UML for system design or DMN for decision modelling. Another way to extend BPMN 2.0 is to incorporate document models, process landscapes, risk catalogs, and IT system models. By doing so, organizations can create a more comprehensive view of their processes and associated risks. Furthermore, to enhance integration with Enterprise Architecture, BPMN 2.0 can be made compliant with ArchiMate. This allows for better alignment of process modelling with enterprise architecture. BPMN 2.0 is capable of serving both technical and professional modelling needs, providing a flexible solution for a wide range of use cases. Finally, by enabling integration with Process Automation and Process Mining, organizations can further enhance the value of their BPMN models.
Summary
BPMN 2.0 serves as a universal language that transcends the barriers within an organization, promoting seamless collaboration and streamlined operations. This notation standard bridges the gaps between various departments by offering an intuitive and standardized way to communicate complex processes. Extension of the metamodel, like ADONIS BPMN Fit for Business, can optimize BPMN’s practicality for everyday use, enabling organizations to identify areas for improvement and optimize the processes. Furthermore, BPMN can be extended and integrated with other modelling languages, broadening its applicability across various scenarios. In essence, BPMN’s standardized visual language is a powerful tool that can enhance communication, transparency, and drive process optimization in your organzation.
Get our weekly updates.
Never miss the freshest content.