Introduction
There’s hardly a process without any flaws. Therefore, it happens time and over again that certain process steps are not executed correctly or are not adhered to – potentially leading to operational discrepancies within the company, or even worse: customer dissatisfaction. Luckily, this really doesn’t have to be the case!
The task here, is to assess whether there’s “merely” a problem with process marketing inside the company, or rather an underlying issue making the said process inadequate or counter-productive. In the latter case, process analysis and optimization come into play to prevent such mistakes in the future and make the process better-fitted to suit the needs of internal and external stakeholders.
Apart from optimization for the sake of continuous improvement, process changes are also a big part of digitalization initiatives as well. Contrary to popular beliefs, introduction of new technologies and ways of working is not where digital transformation stops – it’s actually where it begins. It’s the inclusion in the day-to-day practices, that anchors transformation in the organization in all respects.
But regardless of your reasons for a thorough review of your operational processes, the following blog post will shed light on everything you need to know about process analysis and optimization, from its importance to its benefits to an actionable approach. So don’t miss out on the valuable insights – and keep reading on!
What is Process Analysis & Optimization?
Process analysis is an essential method for understanding how things work, and it is widely used across different fields. Process analysis gained widespread attention as it allows businesses to streamline their operations, increase productivity and ultimately drive growth through process optimization. Its main goal is to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in a process and develop ways to optimize it. Whether it’s through flowcharting, process mapping, process mining or process simulation, process analysis provides a holistic approach to understanding and improving key business processes. It’s a powerful tool that can unlock the full potential of any organization.
In a nutshell, process analysis can be summarized as the systematic examination and deconstruction of a process to get a deeper understanding of it, identify its weaknesses and ways to improve it – ultimately allowing you to foster operational business excellence. Thereby, the goal of process analysis is to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the overall performance. Typically, it would be your first step in the journey of optimizing processes. Process analysis and optimization can also involve the implementation of new technology, such as workflows, ERP systems, RPA and others.
Why is Process Analysis & Optimization important and how does it relate to Business Transformation?
In times of fierce competition and continuous disruption, it is crucial for every business manager, process owner, department head, or team lead to stay on top of their operational processes, constantly. Optimal effectiveness and efficiency of your key processes are essential to sustain your competitive position, and many times can make all the difference between surviving and thriving in the business arena.
That’s why identifying the problem areas and opportunities for improvement are vital first steps in refining your processes and realizing their full potential.
Note that process analysis and business transformation are related, but two very distinct concepts. While process analysis is the systematic examination of a process in order to understand it and identify ways to improve it, business transformation refers to a broader effort to change and improve an organization as a whole.
So in short:
- Business transformation may and typically will include changes to processes, but also may involve changes to organizational structure, culture, and strategy. Business transformation is typically a more comprehensive effort that involves multiple areas of the organization and may take a longer time to implement.
- The goal of process analysis is to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the overall performance. That’s why it typically focuses on a specific process or group of processes within an organization instead.
Both process analysis and business transformation can be used to improve an organization’s performance, but they have different scopes and are used in different situations. One could say that process analysis is a subset of business transformation.
What are the benefits and how can Process Analysis & Optimization improve your business?
There are many benefits of conducting process analysis and optimization within an organization. This typically also depends on the size, maturity and goals of an organization.
Here is a quick look at the most prominent benefits, which are frequently mentioned as the main objective for such initiatives:
Increased efficiency
By identifying and eliminating bottlenecks and inefficiencies in a process, it is possible to increase efficiency and reduce costs. This can help organizations operate more effectively and improve their bottom line.
Improved quality
By identifying and addressing issues that can impact the quality of a process, organizations can improve the quality of the products or services they provide.
Increased customer satisfaction
By understanding a process and identifying areas where it could be made more customer-friendly, organizations can increase customer satisfaction and improve their reputation.
Better compliance
Process analysis can help organizations ensure that their processes are compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
Increased agility
By understanding a process, organizations can identify areas where the process could be made more adaptable to dynamic conditions. This can help organizations be more responsive to changes in the market or in their environment.
Better decision-making
By analysing data from the process, organizations can make better-informed decisions.
Better employee engagement
By involving employees in the process analysis and optimization efforts, organizations can increase employee engagement and create a sense of ownership among them.
Better collaboration
By involving cross-functional team in the process analysis, organizations can foster better collaboration and communication across the different departments.
Overall, process analysis and optimization can help organizations become more efficient, effective, and responsive to changing conditions. It can improve the quality of products and services, increase customer satisfaction, comply with laws and regulations, and foster better collaboration and employee engagement at the same time.
Who should be involved in analysing processes?
A golden rule of process analysis is to go out into the field and talk to the subject matter experts – rather than conceptualizing possible improvements from your own desk, without consulting the most important stakeholders.
To overcome a restricted one-sided perspective, often a cross-functional team of individuals from different areas of the organization is put together to specifically focus on process analysis and optimization initiatives. Which individuals should you involve? Well, that will typically depend on the process you want to analyse, but the group may include:
- Process owners/managers: These are the individuals who are responsible for managing and maintaining the process that is being analysed. They have the most in-depth knowledge of the process and can provide valuable insights into how it can be improved.
- Subject matter experts (SMEs): These are individuals who have specialized knowledge in a specific area that is relevant to the selected process. They can provide valuable insights and expertise on specific aspects of the process.
- Operational staff: These are the individuals who are directly involved in carrying out the process. They have hands-on experience with the process and can provide valuable feedback on what is working well and what is not. Often SMEs come from the operational staff and have some line responsibility, for example team leads.
- Process/Business Analysts: A process analyst is a professional who specializes in analyzing and improving business processes. They use a variety of tools and methodologies to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and other issues within a process, and then work to design and implement solutions that improve its overall performance and effectiveness.
- Management: Managers from different departments, who are responsible and directly involved in the process, should be included in the process analysis and optimization efforts.
- Enterprise Architects, IT team: If the process involves technology, it is important to have IT/Tech experts in the process analysis and optimization efforts.
- Customers: If possible, it is beneficial to also involve customers in the process analysis and optimization efforts. They can provide valuable feedback on how the process affects them and what improvements they would like to see.
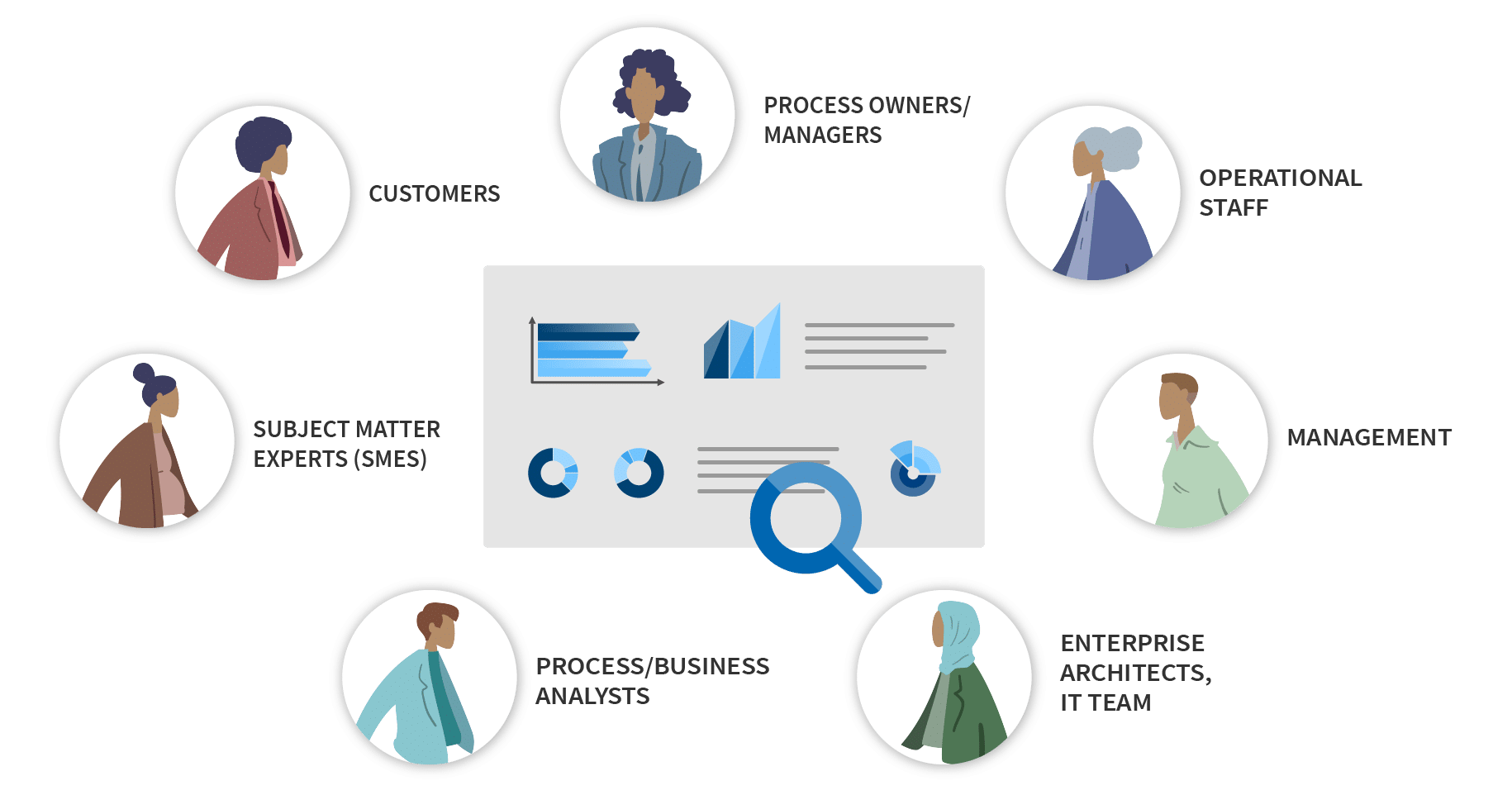
Stakerholders involved in Process Analysis & Optimization
By involving a diverse group of individuals, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the process, identify more opportunities for improvement, and increase buy-in from stakeholders.
How to do Process Analysis & Optimization?
As a first step, begin with writing your processes down, or even better: map them graphically in the form of a process flowchart. That might sound very uninspiring and obvious, but even after 25 years in the BPM business, the following saying definitely holds true: “the first leg of any process optimization initiative lies directly in the process documentation itself”. By noting down the steps, decision points, process paths, responsibilities, handovers, etc., the process analysts can already identify the obvious weaknesses in the process design.
Often, the pure process documentation can already reveal that there is no one, clear process in place – but rather many variants, with tons of exceptions. Writing these processes down, or modelling them in a BPM tool ADONIS, can already help you harmonize these variants and create transparency for all parties involved.
Alternatively, in the case of complex processes and sufficient budget – process mining is another great approach for discovering how processes really run in your organization, thus delivering valuable input for subsequent analysis and optimization.
There are several frameworks and methods used in process analysis, including Process mapping, modelling and simulation, Business Process Reengineering (BPR), Value stream mapping, (Lean) Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM).
Let’s take a closer look at the most common techniques:
Process mapping
This involves creating a visual representation of the process, showing all the steps involved and how they are connected. This can help to identify areas where the process could be simplified or made more efficient.
Process modelling
Business Process modelling involves creating a computer-based model of the process, which can also be used to simulate the process and identify potential for improvements.
Process simulation
This involves using a computer-based model of the process to simulate how the process will behave under different conditions, such as changes in demand or different resource constraints. Process simulation also helps to compare different (should-be) variants of a process model based on defined criteria and therefore provides a base for informed decision-making.
Data analysis
The process data is analysed to identify trends and patterns, which can be used to identify areas where the process could be improved. Process mining is a technique that supports structure data analysis in case the process is already being executed with IT support and so-called event logs are available for such data and consecutive analysis.
If you are interested in practical tips of how to identify optimization potential in your processes, we recommend to check our blog post on business process optimization. There you will also learn in more detail what Process Simulation can do for your organization.
All these frameworks and methods can be used individually or combined to analyse processes and identify areas where improvements can be made. Depending on the specific process, one or more of these techniques may be more appropriate to use to provide a comprehensive approach to process analysis and optimization.
Summary
In essence, process analysis and optimization help to ensure your organization achieves operational excellence and stays on top of its market and competition, in times of disruption and constant change.
By applying the most fitting approach for your organization (and the process at hand), and engaging cross-functional teams to leverage diverse expertise, you can truly future-proof your operations.
If you are looking for advice on how to start your analysis and optimization journey, don’t hesitate to get in touch with our experts. For a further deep dive into process analysis and optimization, be sure to check out our related resources below.









